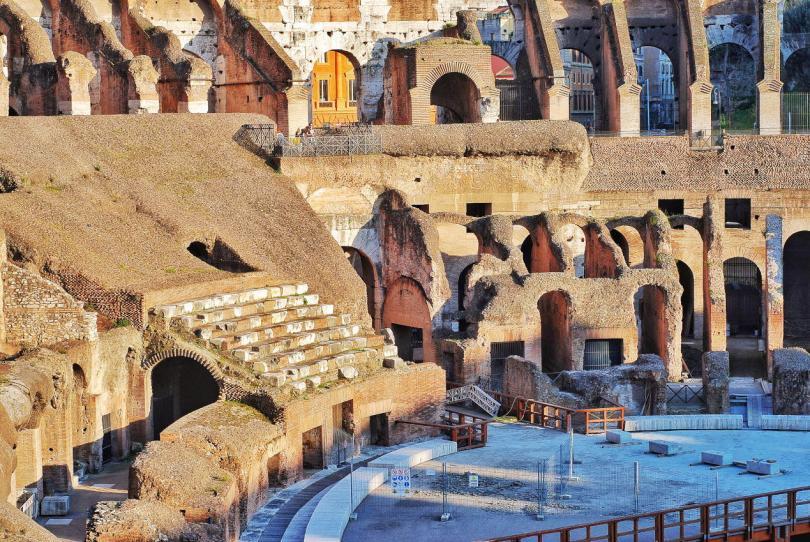
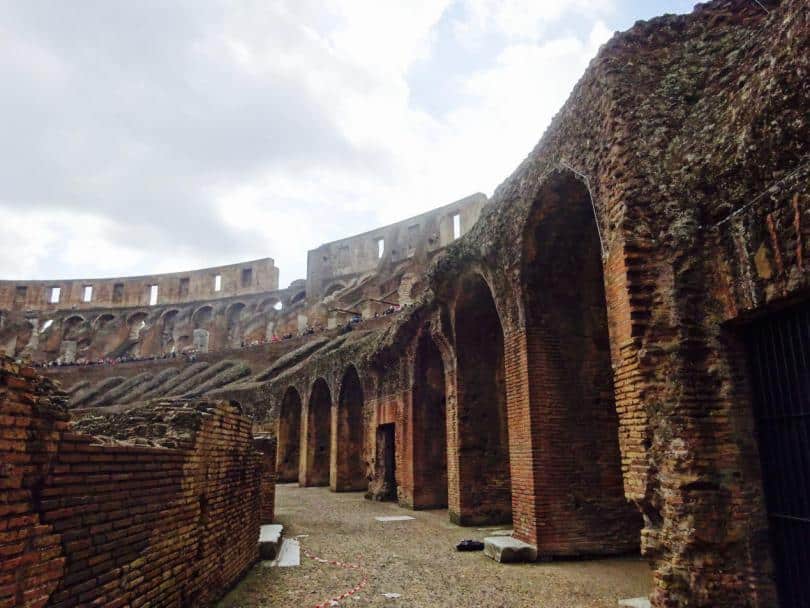
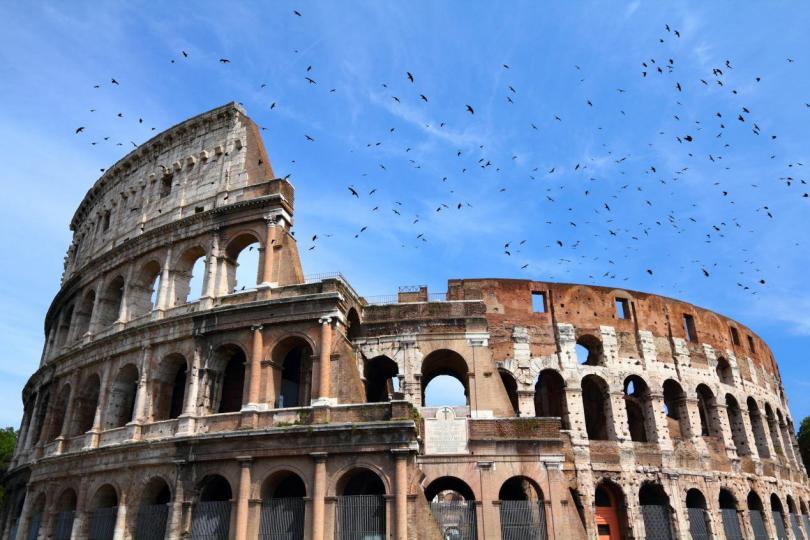
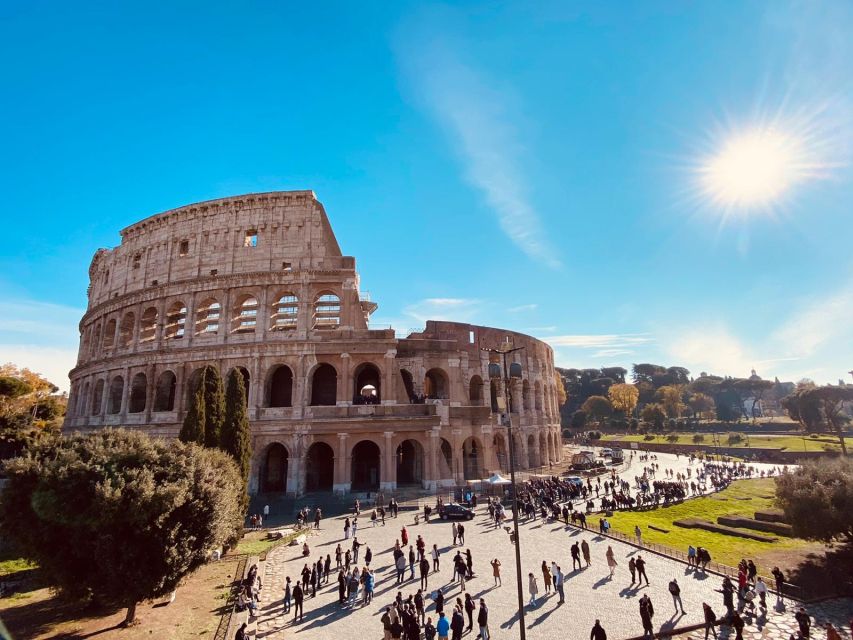
Since the games were public spectacles, entrance was free. However, people needed tickets. The entry tickets told them which entrance to use and where to sit. Each arched entrance had a number carved above it. The number was matched to the entry ticket.
The design of Colosseum was so clever that fifty thousand hurrying people could enter, show their entry tickets, and be seated in 15 minutes.
The stands were divided into sections according to precise social categories. Emperor Augustus carefully regulated the separation of the different classes at all public spectacles.
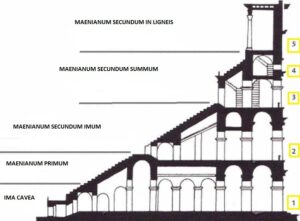
Sections of the Colosseum (Maeniaum)
1 – Ima Cavea (Auditorium)
- This part was reserved for the Emperor, the Senators, Vestal Virgins and the equites.
- Senators’ full names were written specially on their seats.
- Sometimes in this section the magistracies, ambassadors, diplomats, school teachers and their students from noble families ( the Pontifices) were also hosted.
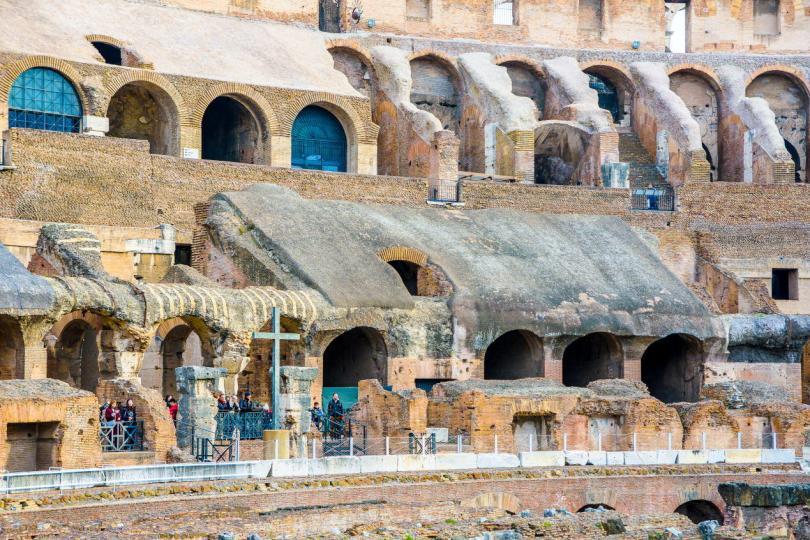
- The Emperor would sit on the place on which now you can see a cross in order to the Christians that died in Colosseum. There was an Imperial Box which was called the “Cubiculum” in which he would use his own chair – the bisellium.
- There were four marble steps.
- There were latrines in this section.
- A fence was stretched around the outside of the arena and rollers & high nets were also hung to protect the spectators.
- Gravediggers, actors and farmer gladiators were not allowed to watch the games.

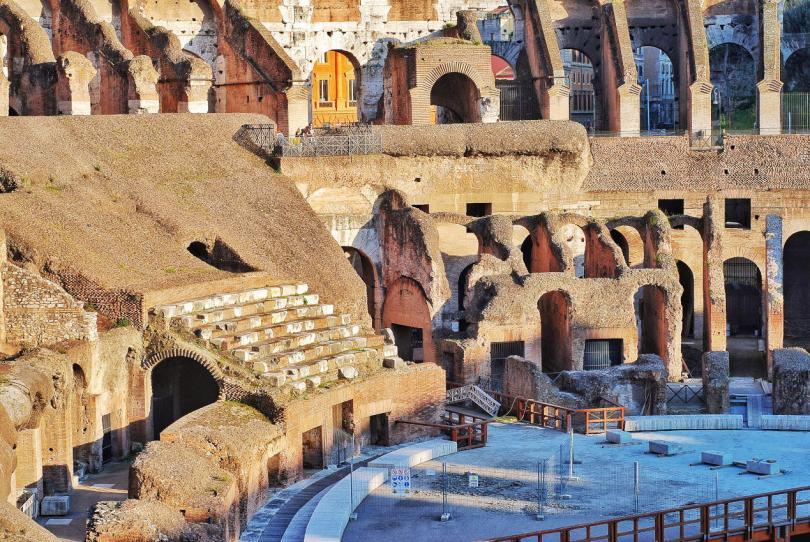
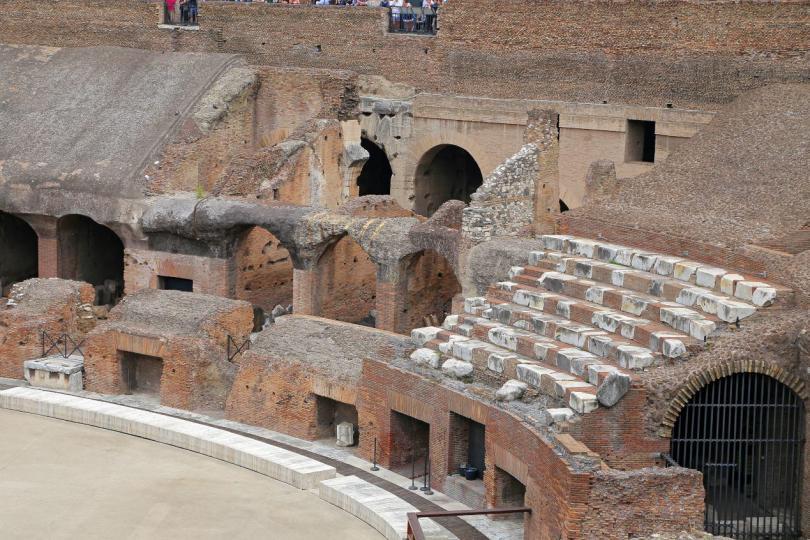
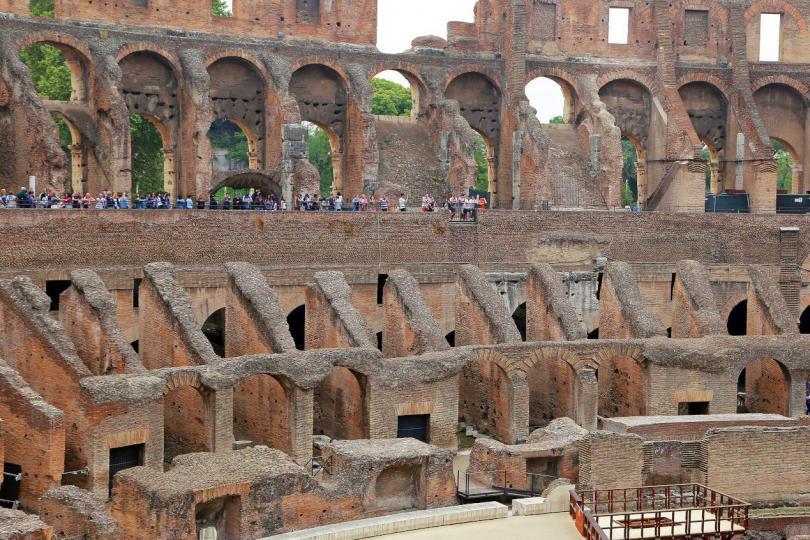
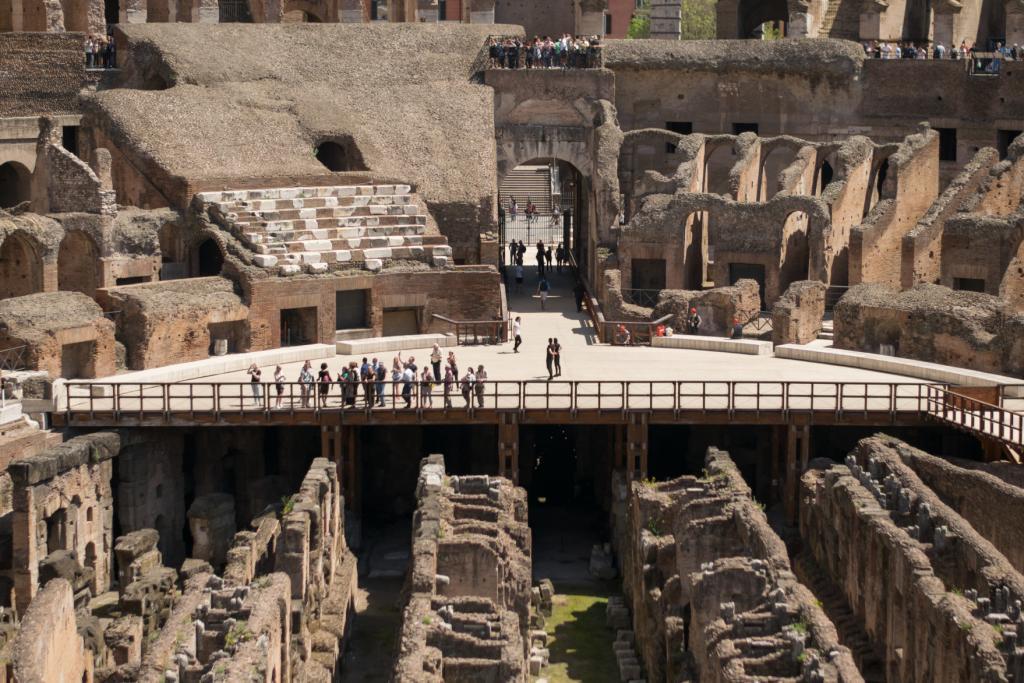
Flavian Amphitheater, interior. East section of the senatorial podium as reconstructed in the 1930’s.
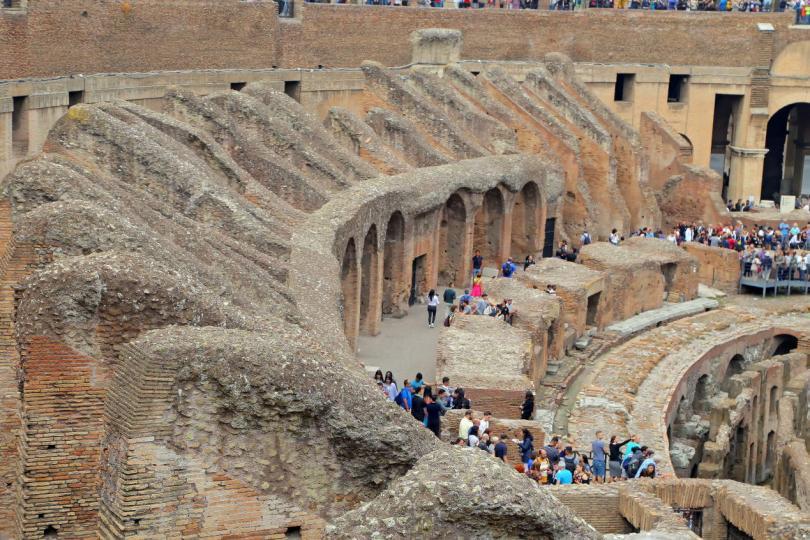
2- Maenianum Primum
- This section had 8/9 marble terraces.
- Generally equites would use this part.
2-a. Maenianum Secundum Imum
- This section had 19/20 terraces.
- This part seperated for the ordinary citizens and plebeians.
2-b Maenianum Secundum Summum
- It had numbered sections.
- There were 10/11 terraces which were selected for poor plebeians.
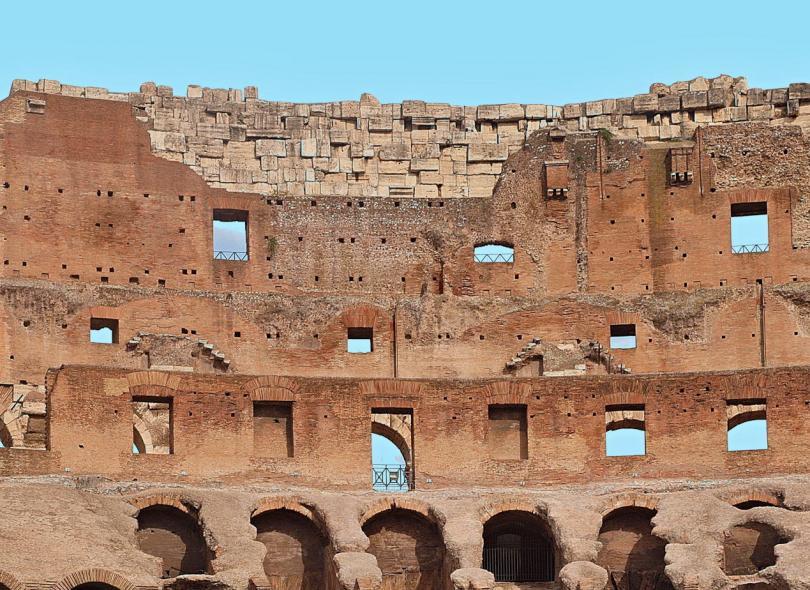
4-Maenianum Secundum in Ligneis
- This section was added during the reign of Domitian.
- It was also known as attic.
- It would host the lowest class of people and slaves.
- These 10/11 wooden terraces would also reduce the stress on the external walls.

Flavian Amphitheater, interior. The service gallery and the inscription regarding the restoration of the stands in the middle of the fifth century A. D. Names of senators are carved on the other side

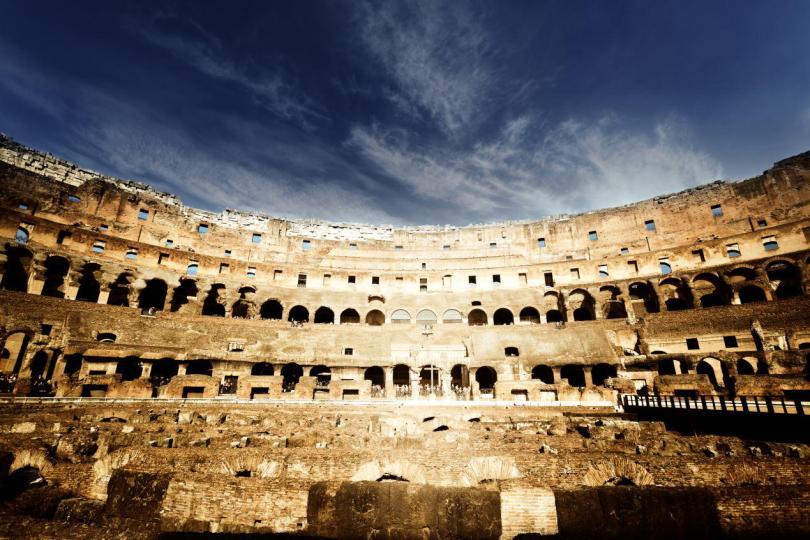
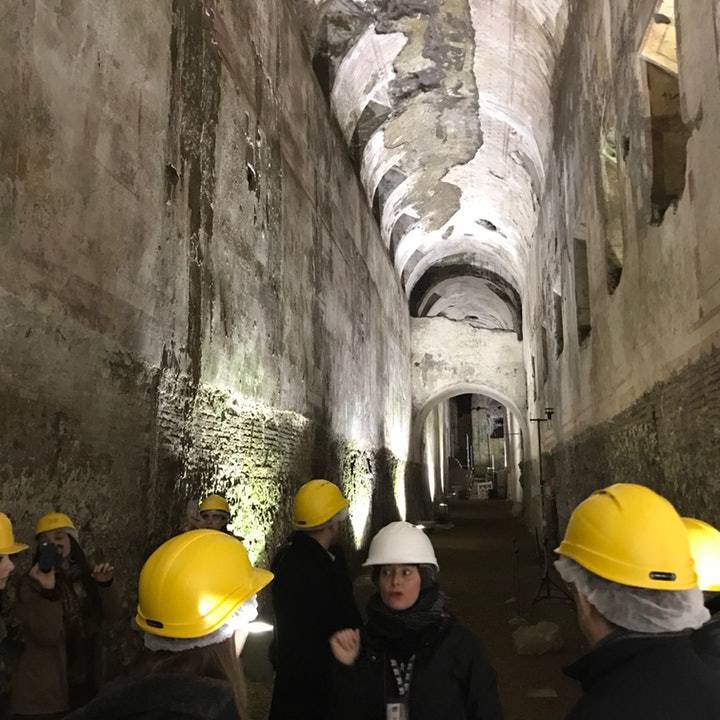
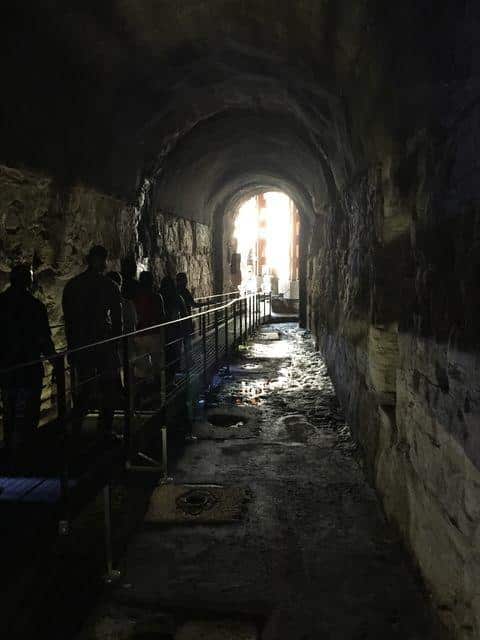
Brick structure that supported the seating terraces over tunnels and walkways that once held tigers and gladiators under the floor of the Colosseum
«Having been outraged by the insult to a senator who, at a crowded show in Puteoli, had not been offered a seat by anyone, [Augustus] ordered regulations to prevent the disorderly and haphazard distribution of seats. He had a senatorial decree issued providing that at every public performance the front row of seats be reserved for senators. He separated soldiers from civilians. He assigned special seats to married commoners and a special section to boys not yet come of age, as well as one to their tutors nearby. He banned badly dressed spectators from the best seats, and confined women to the highest rows, whereas they had previously sat together with men.
He assigned a separate section, facing the praetor’s box, to the Vestal Virgins. He did not allow any women at all to watch athletic contests. Indeed, when the crowd called for a boxing match during the Pontifical Games he postponed it until the following morning, and he issued an edict announcing that he did not want women to go to the theater before ten o‘clock»
(Suetonius, August, 44, 3-4).Seating terraces and the underground Labyrinth of corridors that once held tigers and gladiators under the floor of the Colosseum